Microdiscectomy vs Laminectomy
Microdiscectomy and laminectomy are both spine surgeries done to decompress the spinal nerve roots. The compression may be caused by herniation of the intervertebral disc or narrowing of the intervertebral foramen. While microdiscectomy surgery is performed to remove the herniated intervertebral disc, laminectomy surgery is usually performed to increase the space of the neural foramen.
The spinal cord runs from the lower part of the brain and ends around the lower border of the L1/L2 vertebrae. The spinal cord runs as a bunch of spinal nerves below L1/L2 known as cauda equina. The spinal cord/dural sac is contained inside the central canal formed by the vertebrae. The individual vertebrae are separated from each other by the intervertebral disc.
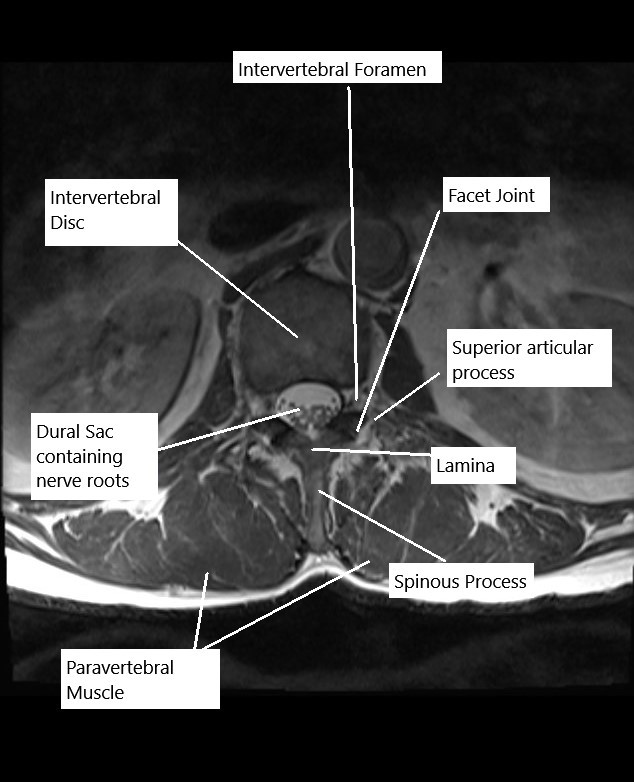
MRI of the lumbar spine in axial section.
The intervertebral disc has watery consistency in its center with a firm outer ring. The intervertebral disc serves to cushion the impact between the adjoining vertebrae. At each segment, spinal nerves exit the vertebral column through the intervertebral foramen. The intervertebral foramen is surrounded by the intervertebral disc, lamina, and facet joints.
Disc herniation known as the prolapsed intervertebral disc (PIVD) may compress the dural sac/ spinal nerves. The prolapse of the disc material may also narrow the intervertebral foramen. The intervertebral disc undergoes changes with advancing age in the form of decreased water content and minor cracks in the outer ring. With repetitive motion or due to sudden trauma the inner soft material may herniate through the outer ring.
The compression of the dural sac or the spinal nerve roots leads to symptoms of radiating pain also known as Conservative management. The sciatica symptoms may include a tingling sensation in the lower extremities. In severe cases of compression, there may be symptoms of numbness and weakness in the legs.
Patients with neural canal narrowing known as lumbar canal stenosis often experience pain in the legs upon walking and bending backward. The pain in the legs in walking does not get better with rest and instead subsides only on bending forward. Similarly, patients may complain of pain on descending a flight of stairs but with no symptoms on ascending.
The unique symptoms of lumbar canal stenosis are due to the anatomical makeup of the lumbar spine. The space inside the neural foramen narrows on bending backward. With a herniated disc, the precarious space is further narrowed on extending the spine leading to symptoms of claudication.
The initial management of sciatica is conservative. Conservative management is done in the form of modification of activity, pain relief medications such as ibuprofen, and heat/cold therapy. Once the initial inflammatory phase resolves, physical therapy may be initiated to help in strengthening the back muscles.
In patients with continued symptoms, nerve root injections or caudal epidural injections may be tried. Surgical treatment in the form of microdiscectomy or laminectomy is done when all forms of conservative management have been tried and failed.
During microdiscectomy surgery, the spine surgeon gives a small incision in the lower back while the patient is under general anesthesia. The surgery may also be done in an outpatient setting with local anesthesia depending upon the patient’s underlying condition.
The surgeon uses magnifying glasses and an endoscope to visualize the surgical field through a small incision. The muscles are carefully separated and the lamina is identified. A small fragment of the lamina is removed to visualize the intervertebral disc.
The surgeon then uses an instrument to carefully take small bites of the disc material until the disc herniation is removed. During the process, the nerve roots are protected using careful retraction. The surgeon closes the incision in layers and a small tape is applied at the incision site.
The laminectomy surgery may be a part of the microdiscectomy surgery while removal of the herniated disc or be done to increase the space of the canal. During surgery, the surgeon gives an incision at the back at a level determined preoperatively. The muscles and tissues are carefully separated.
A part ligamentum flavum is removed. The lamina is then removed to increase the space available for the neural tissues. The lamina may be partially removed known as a laminotomy or completely removed on one side known as a laminectomy. The lamina may also be opened up to create a hinge (laminoplasty) to allow more space for the neural structures.
The surgeon may perform laminectomy only on one side or may perform on both sides. During the surgery, if the surgeon determines any instability of the spinal segment, fusion surgery may be performed.
Similar to microdiscectomy, the majority of the patients undergoing laminectomy are able to go home the same day of the procedure. With minimally invasive techniques such as endoscopic laminectomy, the recovery is short and the patients are able to return to their activities sooner.
Both the microdiscectomy and the laminectomy surgery are aimed to relieve the symptoms of sciatica. The type of surgery required is dependent upon the patient’s underlying cause of lumbar radiculopathy. Both the surgeries are highly successful in treating sciatica. Your spine surgeon will discuss the type of surgery and the outcomes before the procedure.
Do you have more questions?
Which procedure has a faster recovery time?
Microdiscectomy generally has a faster recovery time due to its minimally invasive nature and smaller incisions.
What are the main benefits of a microdiscectomy?
Benefits include smaller incisions, reduced tissue damage, less postoperative pain, and a quicker recovery period.
When is laminectomy preferred over microdiscectomy?
Laminectomy is preferred for patients with severe spinal stenosis or significant spinal canal narrowing that requires extensive decompression.
What are the potential complications of a laminectomy?
Complications can include infection, blood clots, nerve damage, and spinal instability.
How long is the typical hospital stay for each procedure?
Hospital stays for microdiscectomy are usually shorter, often just one day, while laminectomy may require a longer stay, typically 1-3 days.
What is the success rate of microdiscectomy in relieving pain?
Microdiscectomy has a high success rate, with most patients experiencing significant relief from leg pain (sciatica).
Can these procedures be performed on an outpatient basis?
Microdiscectomy is often performed as an outpatient procedure. Laminectomy typically requires an inpatient stay but can sometimes be outpatient depending on the extent of the surgery and patient health.
What is the recovery process like for microdiscectomy?
Recovery involves gradual resumption of activities, physical therapy, and avoiding heavy lifting or twisting movements for several weeks.
How soon can I return to work after a microdiscectomy?
Many patients can return to light work within 2-4 weeks, but this varies based on the nature of their job and individual recovery.
What activities should be avoided after a laminectomy?
Patients should avoid heavy lifting, bending, twisting, and high-impact activities until cleared by their surgeon.
Is physical therapy necessary after these surgeries?
Yes, physical therapy is often recommended to help strengthen the back and improve flexibility.
How do I manage pain after surgery?
Pain management may include medications, ice packs, and gentle stretching exercises as advised by your surgeon.
Will I need any special equipment at home after surgery?
You may need a walker or cane for mobility, a raised toilet seat, and possibly a shower chair to aid in recovery.
What are the signs of a potential complication after surgery?
Signs include increased pain, redness or swelling at the incision site, fever, or any new neurological symptoms like numbness or weakness.
How effective is laminectomy in treating spinal stenosis?
Laminectomy is highly effective in relieving symptoms of spinal stenosis, particularly leg pain and weakness.
What are the long-term outcomes of microdiscectomy?
Long-term outcomes are generally positive, with many patients returning to their normal activities without recurrence of symptoms.
Can I expect complete relief of symptoms after these surgeries?
Many patients experience significant symptom relief, though some may have residual pain or other symptoms depending on the severity and duration of their condition.
How do these procedures affect the spine’s stability?
Microdiscectomy typically does not affect spinal stability significantly. Laminectomy may slightly reduce stability, sometimes requiring spinal fusion
What lifestyle changes should I make after surgery?
Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can help prevent recurrence of spinal issues.
Are there any alternatives to these surgeries?
Alternatives include physical therapy, medications, epidural steroid injections, and less invasive procedures like percutaneous discectomy.
How do I know if I am a candidate for microdiscectomy?
Candidates typically have a herniated disc causing significant nerve compression and have not responded to conservative treatments like physical therapy or medications.
How soon can I start driving after surgery?
Patients can typically resume driving once they are no longer taking narcotic pain medications and feel comfortable, usually around 2-4 weeks post-surgery.
What kind of anesthesia is used during these surgeries?
Both procedures are usually performed under general anesthesia.

Dr. Suhirad Khokhar
My name is Dr. Suhirad Khokhar, and am an orthopaedic surgeon. I completed my MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery) at Govt. Medical College, Patiala, India.
I specialize in musculoskeletal disorders and their management, and have personally approved of and written this content.
My profile page has all of my educational information, work experience, and all the pages on this site that I've contributed to.
